“Navigating Consumer Data Privacy: What Businesses Must Know—and What You Should Expect.”
Understanding Consumer Data Privacy Laws: Key Regulations and Their Impact on Businesses
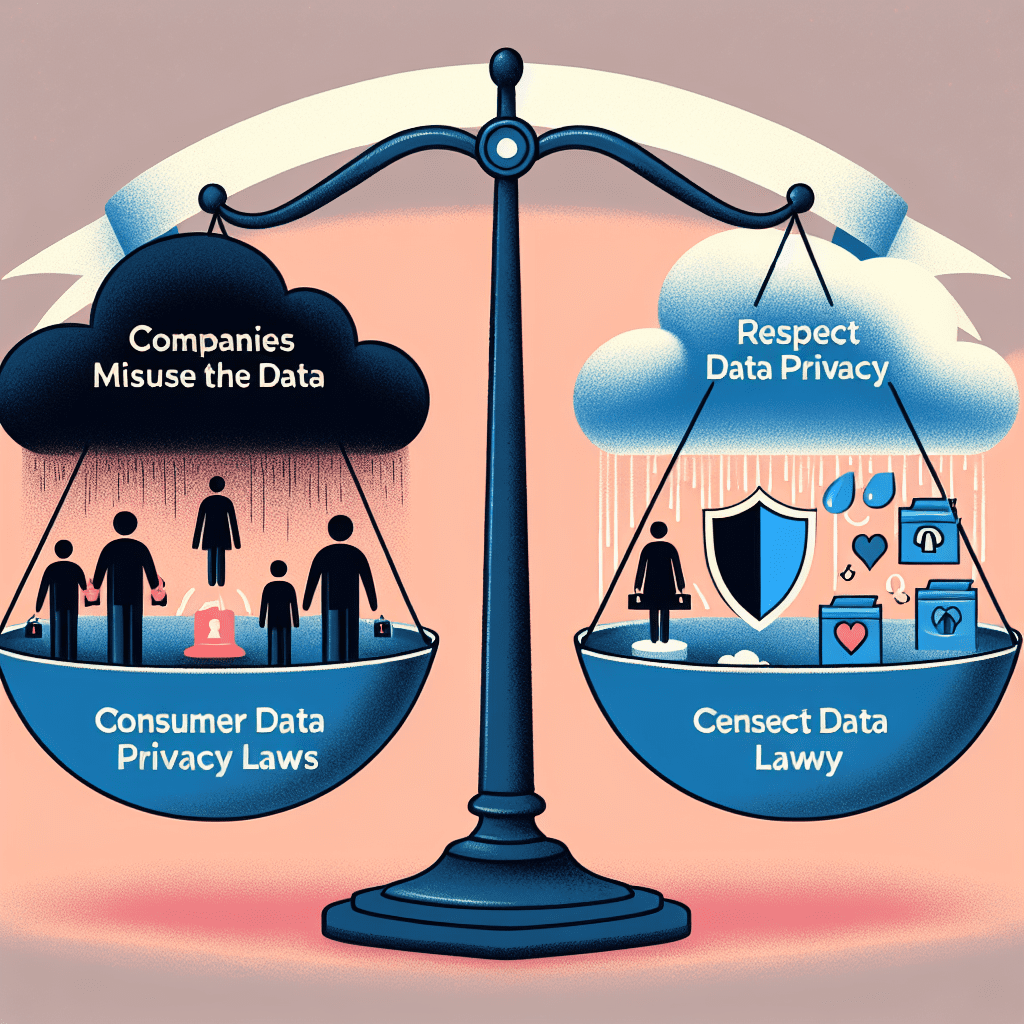
Consumer data privacy laws have become a critical aspect of modern business operations, shaping how companies collect, store, and use personal information. As digital interactions increase, governments worldwide have introduced regulations to protect individuals from unauthorized data usage and potential breaches. These laws not only safeguard consumer rights but also impose strict compliance requirements on businesses, influencing their data management practices and operational strategies.
One of the most influential regulations in this space is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), implemented by the European Union in 2018. The GDPR establishes stringent guidelines on data collection, requiring companies to obtain explicit consent before processing personal information. It also grants individuals the right to access, correct, and delete their data, ensuring greater transparency and control. Non-compliance can result in severe financial penalties, compelling businesses to adopt robust data protection measures. Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), enacted in the United States, provides consumers with the right to know what data is being collected, opt out of its sale, and request its deletion. The CCPA has set a precedent for other states, leading to the emergence of additional privacy laws across the country.
Beyond these regulations, other jurisdictions have introduced their own frameworks to address data privacy concerns. For instance, Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD) closely mirrors the GDPR, emphasizing consumer rights and corporate accountability. Meanwhile, Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) mandates that businesses obtain informed consent before collecting personal data and implement safeguards to prevent unauthorized access. These laws collectively reflect a global shift toward prioritizing consumer privacy, requiring companies to align their practices with evolving legal standards.
For businesses, compliance with these regulations presents both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, organizations must invest in data protection infrastructure, update privacy policies, and train employees on regulatory requirements. Failure to do so can result in reputational damage and financial penalties, making compliance a top priority. On the other hand, adhering to privacy laws can enhance consumer trust, as individuals are more likely to engage with companies that demonstrate a commitment to protecting their personal information. By implementing transparent data practices, businesses can differentiate themselves in a competitive market and foster long-term customer relationships.
Despite these legal protections, companies still have certain rights regarding data usage, provided they operate within regulatory boundaries. Many privacy laws allow businesses to collect and process data for legitimate purposes, such as improving services, conducting research, and ensuring security. However, they must clearly communicate these purposes to consumers and offer mechanisms for opting out when applicable. Additionally, anonymized or aggregated data, which does not identify specific individuals, can often be used more freely for analytical and business intelligence purposes.
As consumer awareness of data privacy grows, regulatory frameworks will likely continue to evolve, introducing new compliance requirements for businesses. Companies must stay informed about legislative changes and proactively adjust their data management strategies to remain compliant. By prioritizing transparency, security, and ethical data practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of consumer data privacy laws while maintaining trust and credibility in an increasingly regulated digital landscape.
What Companies Can and Can’t Do with Your Data: Navigating Compliance in the Digital Age

As consumer data privacy laws continue to evolve, companies must carefully navigate the complex landscape of compliance while maintaining their ability to leverage data for business operations. With regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, organizations face increasing scrutiny over how they collect, store, and use personal information. These laws establish clear guidelines on what companies can and cannot do with consumer data, ensuring greater transparency and control for individuals while imposing strict obligations on businesses.
One of the fundamental principles of modern data privacy laws is the requirement for informed consent. Companies must obtain explicit permission before collecting personal data, and they must clearly communicate how that data will be used. This means that businesses can no longer rely on vague or overly broad privacy policies; instead, they must provide detailed disclosures that allow consumers to make informed decisions. Additionally, individuals have the right to withdraw their consent at any time, requiring companies to implement mechanisms that facilitate such requests efficiently.
Beyond consent, organizations are also subject to limitations on data collection and processing. They can only gather information that is necessary for a specific, legitimate purpose, and they must ensure that data is not used in ways that exceed the original intent. For example, a company collecting email addresses for account verification cannot later use that information for marketing purposes without obtaining additional consent. This principle, known as purpose limitation, prevents businesses from exploiting consumer data for unintended uses.
Moreover, data minimization is another key requirement under privacy regulations. Companies must collect only the minimum amount of personal information necessary to fulfill their stated purpose. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access while ensuring that businesses do not accumulate excessive amounts of sensitive information. In practice, this means that organizations must regularly review their data collection practices and eliminate any unnecessary data points.
In addition to these restrictions, companies are also responsible for implementing robust security measures to protect consumer data. Regulations mandate that businesses take appropriate steps to safeguard personal information from unauthorized access, loss, or theft. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities. Failure to implement adequate security measures can result in severe penalties, as well as reputational damage that may erode consumer trust.
On the other hand, privacy laws also grant consumers significant rights over their personal data. Individuals have the right to access the information that companies hold about them, request corrections to inaccurate data, and even demand the deletion of their personal information under certain circumstances. Businesses must establish processes to handle these requests promptly and transparently, ensuring compliance with legal requirements while maintaining positive customer relationships.
Despite these stringent regulations, companies still have opportunities to use consumer data within legal boundaries. Aggregated and anonymized data, for instance, can be analyzed for business insights without violating privacy laws. Additionally, businesses can leverage first-party data—information collected directly from consumers with their consent—to personalize experiences and improve services. However, they must always ensure that their data practices align with regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
As data privacy laws continue to expand globally, companies must remain vigilant in adapting to new compliance obligations. By prioritizing transparency, security, and consumer rights, businesses can not only avoid legal repercussions but also build trust with their customers. In an era where data privacy is a growing concern, organizations that demonstrate a commitment to ethical data practices will be better positioned for long-term success.
The Future of Consumer Data Privacy: Emerging Trends and How Businesses Should Prepare
As consumer awareness of data privacy continues to grow, governments worldwide are enacting stricter regulations to protect personal information. The future of consumer data privacy is evolving rapidly, with emerging trends shaping how businesses collect, store, and use customer data. Companies must stay ahead of these changes to ensure compliance while maintaining customer trust. Understanding these trends and preparing for the shifting regulatory landscape will be essential for businesses that rely on data-driven strategies.
One of the most significant trends in consumer data privacy is the expansion of comprehensive privacy laws. Regulations such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have set a precedent for other jurisdictions. Countries and states are increasingly adopting similar frameworks, granting consumers greater control over their personal information. These laws often include provisions that allow individuals to access, correct, or delete their data, as well as opt out of data collection practices. As more regions implement such regulations, businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions must navigate a complex web of compliance requirements.
In addition to regulatory expansion, there is a growing emphasis on data minimization and purpose limitation. Companies are being encouraged—or in some cases, required—to collect only the data necessary for a specific purpose and to avoid excessive data retention. This shift is driven by concerns over data breaches and unauthorized access, which have become more frequent in recent years. By limiting the amount of personal information they collect and store, businesses can reduce their risk exposure while demonstrating a commitment to consumer privacy.
Another emerging trend is the increasing use of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs). These tools, such as encryption, anonymization, and differential privacy, help businesses protect consumer data while still deriving valuable insights. For example, differential privacy allows organizations to analyze trends in large datasets without exposing individual user information. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies, companies that invest in PETs will be better positioned to comply with evolving privacy laws while maintaining their ability to leverage data for business intelligence.
At the same time, consumer expectations regarding transparency and control are rising. Individuals are demanding clearer explanations of how their data is used and greater autonomy over their personal information. In response, businesses are implementing more user-friendly privacy policies and consent mechanisms. Some companies are also adopting privacy-by-design principles, integrating data protection measures into their products and services from the outset. By prioritizing transparency and user control, businesses can foster trust and differentiate themselves in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
Looking ahead, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in data privacy will become more prominent. AI-driven tools can help businesses automate compliance processes, detect potential privacy risks, and enhance data security. However, AI also presents challenges, particularly in areas such as algorithmic bias and automated decision-making. Regulators are beginning to address these concerns, and businesses must ensure that their AI systems align with ethical and legal standards.
To prepare for the future of consumer data privacy, businesses should take a proactive approach. Conducting regular privacy assessments, staying informed about regulatory developments, and investing in secure data management practices will be crucial. Additionally, fostering a culture of privacy within an organization—through employee training and clear internal policies—can help mitigate risks and ensure compliance. As privacy laws continue to evolve, companies that prioritize responsible data practices will not only avoid legal penalties but also strengthen their relationships with consumers in an increasingly data-conscious world.