“Find the Perfect Loan for Your Needs – A Complete Guide to Making the Right Choice!”
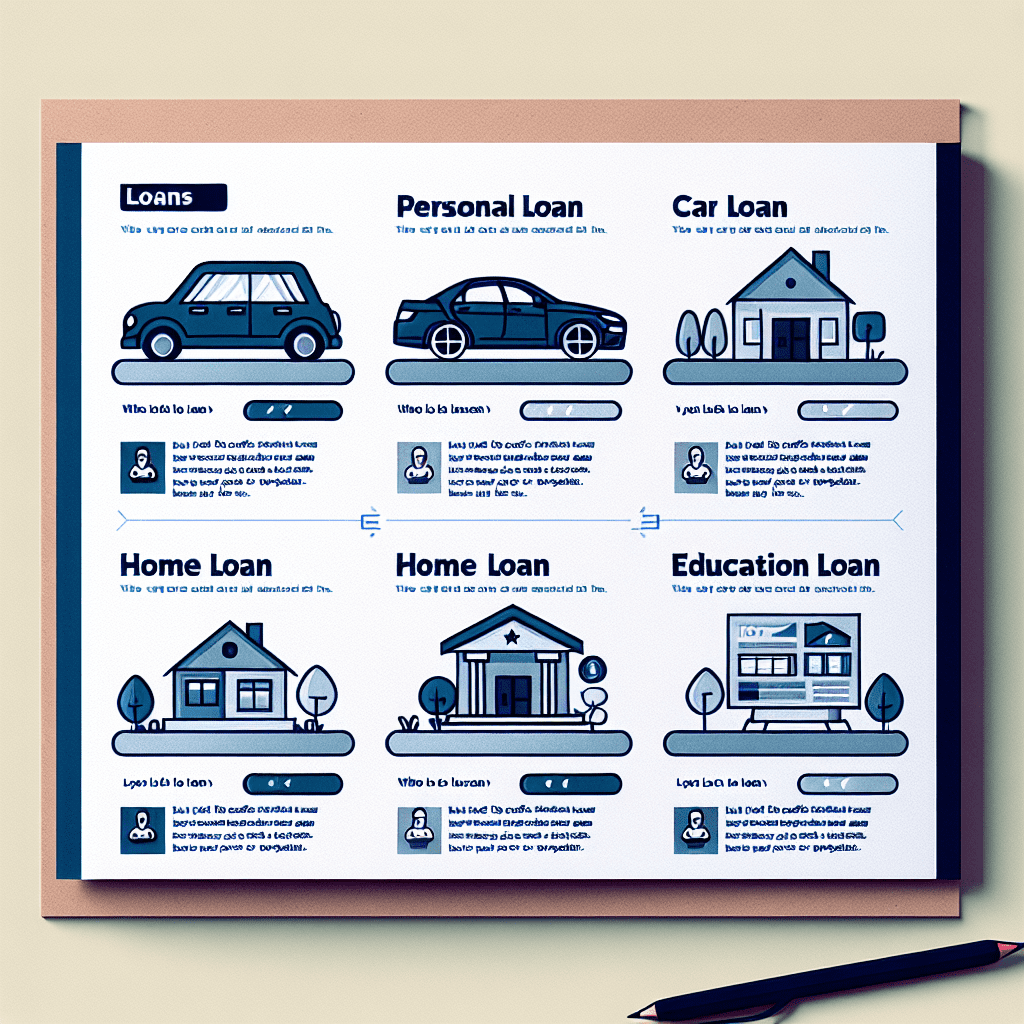
Understanding Different Types of Loans: Which One Suits Your Needs?
When considering a loan, it is essential to understand the different types available and determine which one best suits your financial needs. Loans come in various forms, each designed for specific purposes, and selecting the right one can significantly impact your financial stability. By carefully evaluating your options, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your goals and repayment capacity.
One of the most common types of loans is a personal loan, which offers flexibility in terms of usage. These loans are typically unsecured, meaning they do not require collateral, and they can be used for a variety of purposes, such as consolidating debt, covering medical expenses, or financing a major purchase. Since personal loans are based on creditworthiness, individuals with higher credit scores often receive lower interest rates. However, those with lower credit scores may face higher rates or stricter approval requirements.
In contrast, secured loans require collateral, such as a home or vehicle, to back the loan. A mortgage, for example, is a secured loan specifically designed for purchasing real estate. Because the property itself serves as collateral, mortgage loans generally offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms. Similarly, auto loans are secured loans used to finance vehicle purchases, with the car serving as collateral. While secured loans often provide more favorable terms, they also carry the risk of asset loss if the borrower fails to meet repayment obligations.
For those pursuing higher education, student loans are a specialized option designed to cover tuition, books, and living expenses. These loans can be obtained from government programs or private lenders, with federal student loans typically offering lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options. Many government-backed student loans also provide benefits such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs, making them a preferred choice for many borrowers. However, private student loans may be necessary for those who need additional funding beyond federal limits, though they often come with higher interest rates and fewer borrower protections.
Another widely used loan type is a business loan, which helps entrepreneurs and business owners finance operations, expansion, or equipment purchases. Business loans can be secured or unsecured, depending on the lender’s requirements and the borrower’s credit profile. Small business owners may also explore government-backed loans, such as those offered by the Small Business Administration (SBA), which provide favorable terms and lower interest rates. Choosing the right business loan depends on factors such as the company’s financial health, the purpose of the loan, and the repayment structure.
For homeowners looking to access the equity in their property, home equity loans and home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) are viable options. A home equity loan provides a lump sum amount with a fixed interest rate, while a HELOC functions as a revolving credit line with variable interest rates. Both options allow homeowners to leverage their property’s value for expenses such as home renovations, debt consolidation, or major life events. However, since these loans use the home as collateral, failure to repay could result in foreclosure.
Ultimately, selecting the right loan depends on your financial situation, creditworthiness, and intended use of the funds. By carefully assessing the terms, interest rates, and repayment conditions of each loan type, you can make a well-informed decision that supports your financial goals while minimizing potential risks.
Personal Loans vs. Business Loans: Choosing the Right Option for You
When considering a loan, it is essential to determine whether a personal loan or a business loan best suits your financial needs. Both options provide access to funds, but they serve distinct purposes and come with different terms, eligibility requirements, and repayment structures. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision and ensure that you choose the most appropriate financing option for your situation.
A personal loan is typically used for individual expenses such as debt consolidation, medical bills, home improvements, or major purchases. These loans are generally unsecured, meaning they do not require collateral, and they are based primarily on the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lenders assess factors such as credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio to determine eligibility and interest rates. Because personal loans are not tied to a specific business purpose, they offer flexibility in how the funds can be used. Additionally, they often have fixed interest rates and predictable monthly payments, making them a manageable option for borrowers who need financial stability.
On the other hand, a business loan is specifically designed to support business-related expenses, such as purchasing equipment, expanding operations, or managing cash flow. Unlike personal loans, business loans may be secured or unsecured, depending on the lender’s requirements and the borrower’s financial profile. Secured business loans require collateral, such as business assets or real estate, which can help lower interest rates and increase borrowing limits. Unsecured business loans, while not requiring collateral, often come with higher interest rates and stricter eligibility criteria.
One key distinction between personal and business loans is how they impact credit. A personal loan affects the borrower’s personal credit score, as it is issued in their name. This means that late payments or defaults can have long-term consequences on an individual’s financial health. In contrast, a business loan is typically issued in the name of the business, and its repayment history is reported to business credit bureaus. This can help build the company’s credit profile, making it easier to secure future financing. However, in cases where a business lacks an established credit history, lenders may require a personal guarantee, which holds the business owner personally responsible for repayment.
Another important factor to consider is the loan application process. Personal loans generally have a simpler and faster approval process, as they require fewer documents and less scrutiny. Borrowers typically need to provide proof of income, employment details, and credit history. In contrast, business loans often involve a more complex application process, requiring financial statements, business plans, tax returns, and revenue projections. Lenders assess the business’s financial health and potential for growth before approving the loan, which can result in longer processing times.
Ultimately, the choice between a personal loan and a business loan depends on the intended use of the funds and the borrower’s financial situation. If the loan is needed for personal expenses or small-scale financial needs, a personal loan may be the most suitable option due to its flexibility and straightforward application process. However, if the funds are required for business growth or operational expenses, a business loan is likely the better choice, as it is tailored to support business activities and can help establish a strong financial foundation for the company. By carefully evaluating these factors, borrowers can select the loan that best aligns with their financial goals.
Secured vs. Unsecured Loans: Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases
When considering a loan, one of the most important decisions is whether to choose a secured or unsecured option. Each type has distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand their differences before committing to a financial obligation. By evaluating the benefits, risks, and ideal use cases for each, borrowers can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Secured loans require collateral, meaning the borrower must pledge an asset—such as a home, car, or savings account—as security for the loan. Because lenders have a tangible guarantee, these loans typically come with lower interest rates and higher borrowing limits. This makes them an attractive option for individuals seeking large sums of money, such as for purchasing a home or financing a business. Additionally, secured loans often have longer repayment terms, allowing borrowers to manage their payments more effectively. However, the primary risk associated with secured loans is the potential loss of the pledged asset. If the borrower fails to meet repayment obligations, the lender has the right to seize the collateral to recover the outstanding balance. This makes it crucial for borrowers to assess their ability to repay before opting for a secured loan.
On the other hand, unsecured loans do not require collateral, relying instead on the borrower’s creditworthiness and financial history. Because lenders assume a higher risk, these loans generally come with higher interest rates and lower borrowing limits. Common examples include personal loans, credit cards, and student loans. One of the key advantages of unsecured loans is that borrowers do not risk losing personal assets if they default. This makes them a suitable choice for individuals who need quick access to funds without the burden of securing an asset. However, due to the increased risk for lenders, approval for unsecured loans often depends on a strong credit score and stable income. Those with poor credit may face difficulty obtaining favorable terms or may be required to pay significantly higher interest rates.
When determining which type of loan is best suited for a particular need, it is essential to consider the purpose of the loan, financial stability, and risk tolerance. Secured loans are ideal for long-term investments, such as purchasing a home or financing a vehicle, where lower interest rates and extended repayment terms provide financial flexibility. They are also beneficial for individuals looking to consolidate debt at a lower interest rate, as secured loans often offer more favorable terms than high-interest credit cards. Conversely, unsecured loans are better suited for short-term financial needs, such as covering emergency expenses, funding a vacation, or making smaller purchases. They provide quick access to funds without requiring collateral, making them a convenient option for those who qualify.
Ultimately, the choice between secured and unsecured loans depends on individual financial circumstances and goals. While secured loans offer lower costs and higher borrowing limits, they come with the risk of asset forfeiture. Unsecured loans, though more accessible in some cases, often carry higher interest rates and stricter approval requirements. By carefully evaluating these factors, borrowers can select the loan type that best aligns with their needs, ensuring a responsible and well-informed financial decision.