“Understand Personal Loans: How They Work & What to Know Before Borrowing!”
Understanding Personal Loans: Key Features, Benefits, and Risks
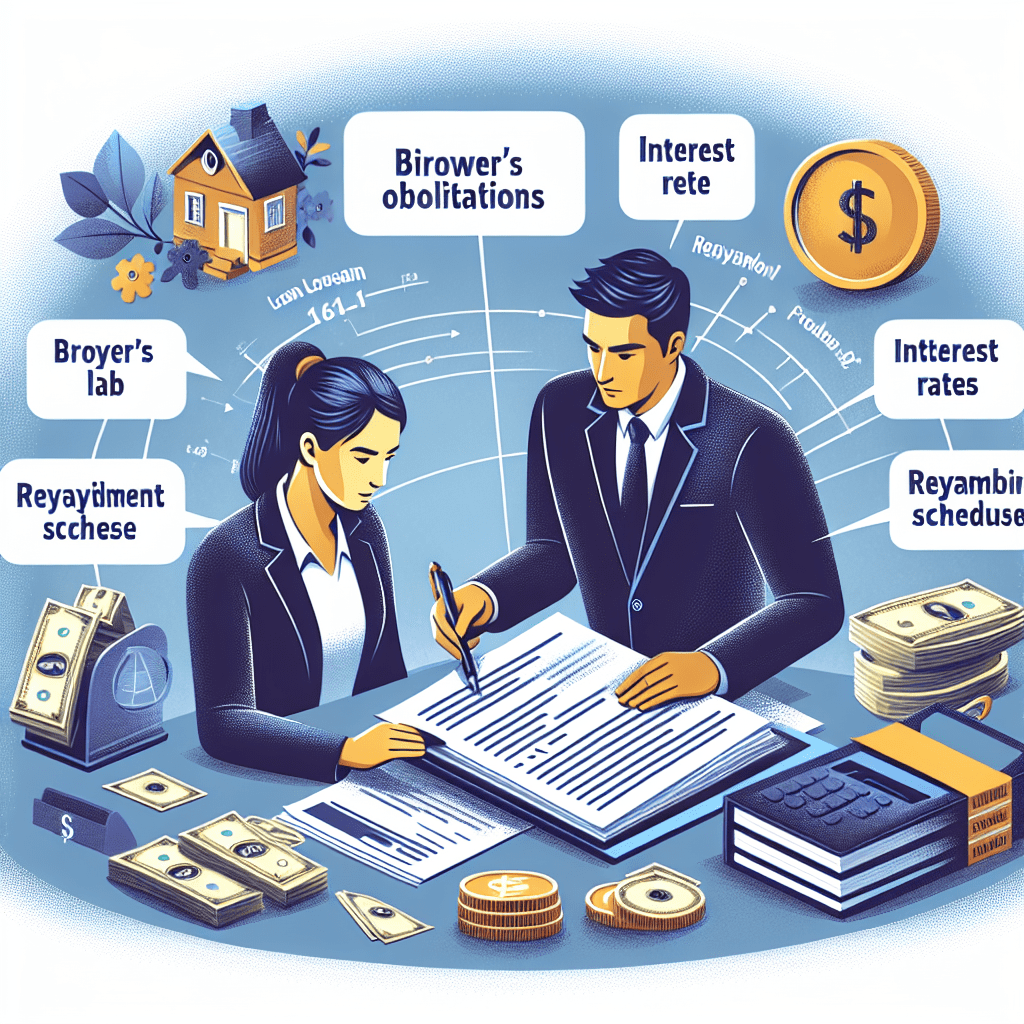
Personal loans are a popular financial tool that allows individuals to borrow a fixed amount of money and repay it over a predetermined period. These loans are typically unsecured, meaning they do not require collateral, and they can be used for a variety of purposes, such as consolidating debt, covering medical expenses, or funding major purchases. Understanding the key features, benefits, and risks associated with personal loans is essential before deciding to borrow, as this knowledge can help individuals make informed financial decisions.
One of the primary features of a personal loan is its fixed repayment structure. Borrowers receive a lump sum upfront and repay it in equal monthly installments over a set term, which can range from a few months to several years. The interest rate on a personal loan may be either fixed or variable, though fixed rates are more common, providing borrowers with predictable payments. Additionally, the loan amount and interest rate are typically determined based on the borrower’s creditworthiness, income, and debt-to-income ratio. Lenders assess these factors to evaluate the borrower’s ability to repay the loan, and those with higher credit scores often qualify for lower interest rates.
Beyond their structured repayment terms, personal loans offer several benefits that make them an attractive option for many borrowers. One significant advantage is their flexibility, as they can be used for almost any financial need. Unlike auto loans or mortgages, which are designated for specific purchases, personal loans provide borrowers with the freedom to allocate funds as needed. Additionally, they often have lower interest rates compared to credit cards, making them a cost-effective option for consolidating high-interest debt. By using a personal loan to pay off multiple credit card balances, borrowers can simplify their payments and potentially reduce the overall interest they pay. Furthermore, personal loans can help improve credit scores when managed responsibly. Making timely payments contributes to a positive payment history, which is a crucial factor in credit scoring models.
However, while personal loans offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain risks that borrowers should carefully consider. One of the primary risks is the potential for high interest rates, particularly for individuals with lower credit scores. Since personal loans are unsecured, lenders mitigate their risk by charging higher interest rates to borrowers who are deemed less creditworthy. This can result in higher overall borrowing costs, making it essential for individuals to compare loan offers and seek the most favorable terms. Additionally, taking on a personal loan increases financial obligations, and failing to make timely payments can lead to late fees, credit score damage, and even legal action in severe cases. Borrowers should assess their financial situation and ensure they have a stable repayment plan before committing to a loan.
Another potential drawback is the presence of fees, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, or late payment charges. Some lenders charge an origination fee, which is deducted from the loan amount before disbursement, reducing the actual funds received. Prepayment penalties may also apply if a borrower decides to pay off the loan early, limiting their ability to save on interest. Understanding these fees and reading the loan agreement carefully can help borrowers avoid unexpected costs.
Ultimately, personal loans can be a valuable financial resource when used wisely, but they require careful consideration. By evaluating the key features, benefits, and risks, borrowers can determine whether a personal loan aligns with their financial goals and make informed decisions that support their long-term financial well-being.
Eligibility and Application Process: How to Qualify for a Personal Loan
Personal loans can be a valuable financial tool for individuals who need funds for various purposes, such as consolidating debt, covering unexpected expenses, or financing major purchases. However, before applying for a personal loan, it is essential to understand the eligibility requirements and the application process to improve the chances of approval. Lenders evaluate several factors to determine whether an applicant qualifies for a loan, and meeting these criteria can significantly impact the terms and interest rates offered.
One of the primary factors that lenders consider is the applicant’s credit score. A credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness, based on their credit history, payment behavior, and overall financial responsibility. Generally, a higher credit score increases the likelihood of loan approval and may also result in lower interest rates. Most lenders prefer borrowers with a credit score of at least 600, though some may require a higher score for more competitive loan terms. Those with lower credit scores may still qualify for a loan, but they may face higher interest rates or stricter repayment terms.
In addition to credit score, lenders assess an applicant’s income and employment status. A stable and sufficient income reassures lenders that the borrower has the financial capacity to repay the loan. Many lenders require proof of income through pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements. Self-employed individuals may need to provide additional documentation, such as profit and loss statements, to verify their earnings. Employment stability is also a crucial factor, as lenders prefer borrowers with a consistent work history. Frequent job changes or gaps in employment may raise concerns about the borrower’s ability to make timely payments.
Another important consideration is the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which measures the percentage of an individual’s monthly income that goes toward debt payments. Lenders use this ratio to assess whether a borrower can manage additional debt responsibly. A lower DTI ratio indicates that a borrower has sufficient income to cover new loan payments, while a higher ratio may suggest financial strain. Most lenders prefer a DTI ratio below 40%, though some may accept higher ratios depending on other financial factors. Reducing existing debt before applying for a personal loan can improve the chances of approval and result in better loan terms.
Once an applicant meets the eligibility requirements, the next step is the application process. This typically begins with researching and comparing different lenders to find the best loan options. Many financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders, offer personal loans with varying interest rates, fees, and repayment terms. It is advisable to review multiple offers and consider factors such as annual percentage rates (APR), loan amounts, and repayment periods before making a decision.
After selecting a lender, the applicant must complete a loan application, which requires providing personal and financial information. This may include details such as name, address, Social Security number, employment history, and income verification. Some lenders conduct a prequalification process, which allows applicants to check their potential loan terms without affecting their credit score. If prequalified, the applicant can proceed with a formal application, which may involve a hard credit inquiry that temporarily impacts their credit score.
Once the application is submitted, the lender reviews the information and determines whether to approve the loan. This process may take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the lender’s policies. If approved, the borrower receives a loan agreement outlining the terms and conditions, including the interest rate, repayment schedule, and any applicable fees. It is crucial to review this agreement carefully before signing to ensure a clear understanding of the loan obligations.
After signing the agreement, the lender disburses the loan funds, typically through direct deposit into the borrower’s bank account. The borrower is then responsible for making regular payments according to the agreed-upon schedule. Timely payments not only help avoid late fees and penalties but also contribute to maintaining a positive credit history. Understanding the eligibility requirements and application process can help borrowers make informed decisions and secure a personal loan that aligns with their financial needs.
Interest Rates and Repayment Terms: What to Consider Before Borrowing
When considering a personal loan, understanding interest rates and repayment terms is essential to making an informed financial decision. These factors directly impact the total cost of borrowing and your ability to manage monthly payments effectively. Before committing to a loan, it is crucial to evaluate how interest rates are determined, how repayment terms affect affordability, and what options best suit your financial situation.
Interest rates on personal loans can vary significantly based on several factors, including your credit score, income, loan amount, and lender policies. Generally, borrowers with higher credit scores receive lower interest rates because they are considered less risky by lenders. Conversely, individuals with lower credit scores may face higher rates, as lenders compensate for the increased risk of default. Additionally, some lenders offer fixed interest rates, which remain constant throughout the loan term, while others provide variable rates that fluctuate based on market conditions. Fixed rates offer predictability, making it easier to budget for monthly payments, whereas variable rates may start lower but can increase over time, potentially leading to higher costs.
Beyond interest rates, repayment terms play a significant role in determining the overall affordability of a personal loan. Loan terms typically range from one to seven years, with shorter terms resulting in higher monthly payments but lower total interest costs. On the other hand, longer terms reduce monthly payment amounts but increase the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Choosing the right repayment term requires balancing affordability with minimizing interest expenses. Borrowers should assess their financial stability and income consistency to ensure they can meet payment obligations without financial strain.
In addition to interest rates and repayment terms, it is important to consider any additional fees associated with the loan. Some lenders charge origination fees, which are deducted from the loan amount before disbursement, while others impose prepayment penalties for paying off the loan early. Understanding these costs in advance can help borrowers avoid unexpected expenses and select a loan that aligns with their financial goals. Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders can also provide insight into the most competitive rates and terms available.
Another key consideration is the impact of a personal loan on overall financial health. Taking on debt requires careful planning to ensure that monthly payments fit within your budget without compromising other financial obligations. Borrowers should calculate their debt-to-income ratio, which measures total monthly debt payments relative to income, to determine whether they can comfortably afford the loan. A high debt-to-income ratio may indicate financial strain and could make it more challenging to secure favorable loan terms.
Furthermore, understanding the consequences of missed or late payments is essential. Late payments can result in additional fees, negatively impact credit scores, and make it more difficult to obtain future credit. Setting up automatic payments or reminders can help borrowers stay on track and avoid potential penalties. If financial difficulties arise, communicating with the lender about possible repayment options or temporary relief programs can prevent further financial hardship.
Ultimately, evaluating interest rates and repayment terms before borrowing a personal loan ensures that borrowers make informed decisions that align with their financial needs. By carefully considering these factors, comparing loan offers, and planning for repayment, individuals can secure a loan that supports their financial goals while minimizing unnecessary costs.